A shortcut join is a join that provides an alternative path between two tables. shortcut joins improve the performance of a query by not taking into account intermediate tables, and so shortening a normally longer join path.
A common use of shortcut joins is to link a shared lookup table to another table further along a join path. The join path comprises several different tables in the same context. In such a case, the shortcut join is only effective when the value being looked up has been denormalized to lower levels in a hierarchy of tables, so the same value exists at all the levels being joined.
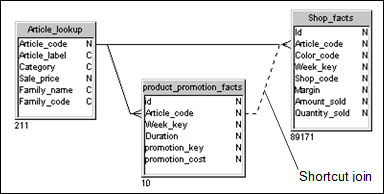
In the following example the column Article_code appears in both the tables Product_Promotion_Facts and Shop_Facts. The value of Article_code is the same for both tables. The normal path for a query using Article_code from Product_Promotion_Facts and Shop_Facts, is to pass through the intermediary table Article_Lookup.

The shortcut join directly linking Product_Promotion_Facts and Shop_Facts allows the query to ignore the intermediary table Article_Lookup, optimizing the query.
 Designer
does not consider shortcut joins during automatic loop and context detection.
However, if you set the cardinality for a shortcut join you avoid receiving
the message 'Not all cardinalities are set' when detecting contexts.
Designer
does not consider shortcut joins during automatic loop and context detection.
However, if you set the cardinality for a shortcut join you avoid receiving
the message 'Not all cardinalities are set' when detecting contexts.